You wake up tired despite sleeping eight hours. Your partner complains about your snoring. You reach for another cup of coffee by 2 PM, wondering why you feel exhausted again.
These aren’t just signs of a busy lifestyle but they could indicate sleep apnea, a serious condition affecting over 22 million Americans. Many people dismiss these symptoms as normal parts of aging or stress, but untreated sleep apnea can lead to heart disease, diabetes, and other health complications.
This guide will help you recognize the warning signs you might be overlooking and explore reliable at-home testing options. You’ll learn when to seek professional help and discover treatment paths that can transform your sleep quality.
What Is Sleep Apnea and Why Should You Care?
Sleep apnea occurs when your breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. The most common type, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), happens when throat muscles relax and block your airway. Central sleep apnea, less common but equally serious, occurs when your brain fails to send proper signals to breathing muscles.
Your body briefly wakes up to restore normal breathing, often without you realizing it. This cycle can repeat hundreds of times per night, preventing deep, restorative sleep your body needs.
The health implications extend far beyond feeling tired. Research shows untreated sleep apnea increases your risk of:
- High blood pressure and heart disease
- Type 2 diabetes
- Stroke
- Depression and anxiety
- Motor vehicle accidents due to daytime drowsiness
Warning Signs You Might Be Missing
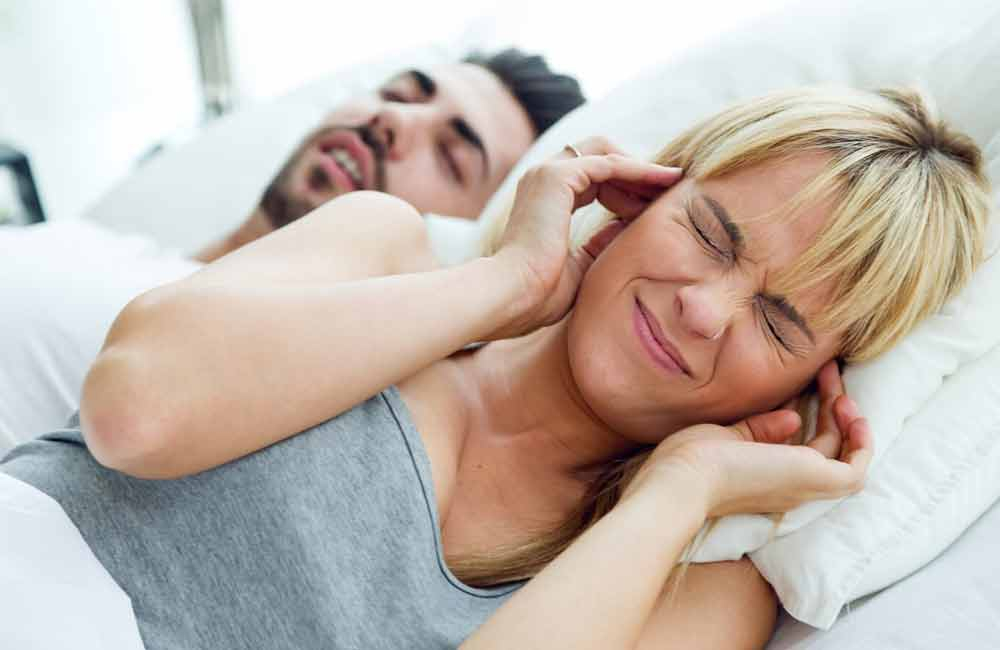

Loud, Chronic Snoring
Not everyone who snores has sleep apnea, but loud, persistent snoring especially when followed by choking or gasping sounds is a major red flag. Partners often notice breathing interruptions before the person with sleep apnea realizes there’s a problem.
Excessive Daytime Fatigue
Feeling tired despite adequate sleep time is one of the most common symptoms. You might find yourself nodding off during meetings, struggling to concentrate, or needing multiple naps throughout the day.
Morning Headaches
Waking up with headaches, particularly those that improve within a few hours, can signal sleep apnea. These headaches result from decreased oxygen levels and increased carbon dioxide in your blood during sleep interruptions.
Mood Changes and Irritability
Sleep apnea affects your emotional regulation. You might notice increased irritability, mood swings, or feelings of depression. The chronic sleep disruption impacts neurotransmitter production, affecting your mental health.
Difficulty Concentrating
Poor sleep quality from sleep apnea impairs cognitive function. You might experience memory problems, difficulty focusing at work, or trouble making decisions. These symptoms often worsen over time without treatment.
Frequent Nighttime Urination
Sleep apnea can disrupt hormones that regulate urine production, leading to more frequent bathroom trips at night. This symptom, called nocturia, often improves with sleep apnea treatment.
Dry Mouth Upon Waking
Mouth breathing during sleep episodes can leave you waking up with a dry mouth or sore throat. This happens because your body attempts to compensate for blocked nasal airways.
Risk Factors That Increase Your Chances
Understanding your risk factors helps determine if you should consider testing for sleep apnea.
Physical Characteristics
Certain physical traits increase sleep apnea risk:
- Excess weight, particularly around the neck
- Large tonsils or adenoids
- Small jaw or receding chin
- Thick neck (17 inches or more in men, 16 inches or more in women)
- Nasal congestion or deviated septum
Demographics
Age and gender play important roles. Sleep apnea becomes more common after age 40, and men are two to three times more likely to develop it than women. However, women’s risk increases after menopause.
Lifestyle Factors
Smoking increases inflammation and fluid retention in airways, tripling your sleep apnea risk. Alcohol and sedatives relax throat muscles, worsening symptoms. Even moderate alcohol consumption before bedtime can trigger sleep apnea episodes.
Medical Conditions
Several health conditions increase sleep apnea risk:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Stroke history
- Hypothyroidism
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Family History
Genetics influence sleep apnea risk through inherited traits like facial structure, tongue size, and obesity predisposition. If family members have sleep apnea, your risk increases significantly.
At-Home Testing: Your Options and What to Expect
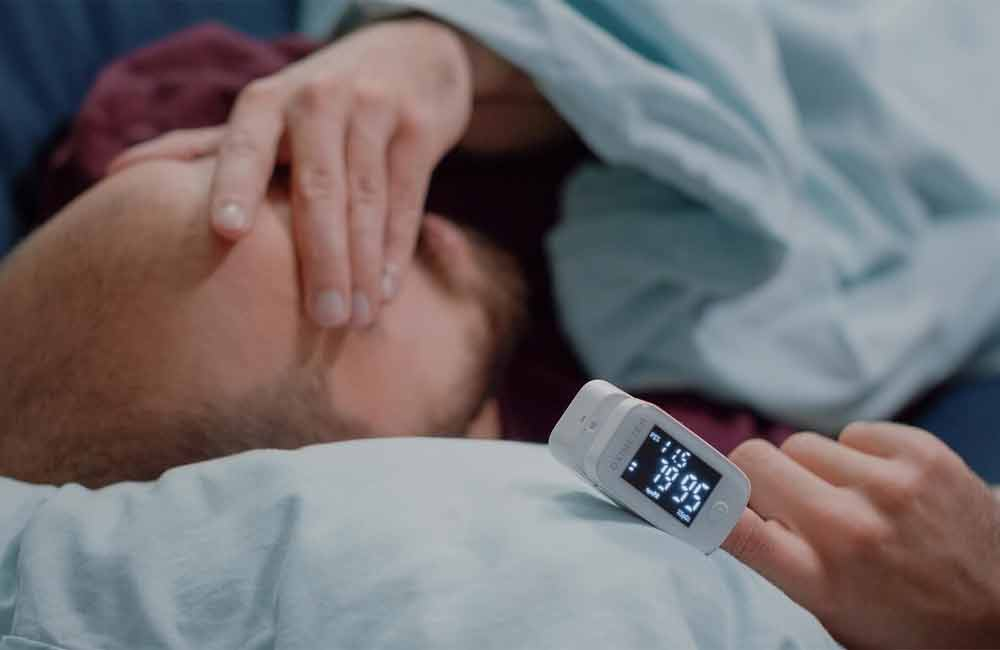

Home sleep apnea tests (HSATs) offer a convenient, cost-effective way to screen for sleep apnea. These tests monitor your breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and sometimes heart rate while you sleep in your own bed.
Types of Home Sleep Tests
Portable Sleep Monitors
These devices typically measure:
- Airflow through your nose and mouth
- Chest and abdominal movement
- Blood oxygen levels
- Heart rate and rhythm
Popular options include WatchPAT, ApneaLink, and ResMed ApneaLink Air. Most require wearing sensors on your finger, chest, and sometimes around your nose.
Smartphone Apps and Wearables
Apps like Sleep Cycle or SnoreLab can track snoring patterns and sleep quality, but they’re not diagnostic tools. Wearable devices like certain Apple Watch models can detect sleep apnea signs, but they supplement rather than replace medical testing.
Pros and Cons of Home Testing
Advantages:
- Sleep in your comfortable environment
- Lower cost than lab studies
- No waiting lists for appointments
- Natural sleep patterns without lab interference
- Results available within days
Limitations:
- Cannot detect all types of sleep apnea
- May miss mild cases
- No technician oversight during testing
- Cannot measure sleep stages or brain activity
- Higher chance of test failure due to sensor displacement
How to Prepare for Home Testing
Maintain your normal routine before testing. Avoid alcohol and sedatives, as they can affect results. Ensure good contact between sensors and your skin, following device instructions carefully.
Most home tests require one to three nights of data collection. If sensors fall off or you sleep poorly, you may need to repeat the test.
When Professional Help Becomes Essential

While home testing provides valuable insights, certain situations require professional evaluation.
Red Flag Symptoms
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Pauses in breathing witnessed by others
- Severe daytime drowsiness affecting daily activities
- Falling asleep while driving or operating machinery
- Chest pain or irregular heartbeat during sleep
Complex Cases
A sleep specialist evaluation is necessary when:
- Home tests are inconclusive
- You have multiple medical conditions
- Previous treatments haven’t worked
- You suspect central sleep apnea
- You need comprehensive sleep disorder evaluation
Insurance and Diagnosis
Most insurance plans cover sleep apnea testing and treatment when medically necessary. A formal diagnosis requires interpretation by a sleep medicine physician, even with home test results.
Treatment Pathways That Actually Work
Effective sleep apnea treatment often combines multiple approaches tailored to your specific situation.
Lifestyle Modifications

Weight Management
Even modest weight loss can significantly improve sleep apnea symptoms. Losing 10% of body weight can reduce the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) by 25% or more in some patients.
Sleep Position Changes
Sleeping on your side instead of your back can reduce symptoms. Positional therapy devices or simple solutions like tennis balls sewn into pajama backs can help maintain side sleeping.
Alcohol and Smoking Cessation
Eliminating alcohol before bedtime and quitting smoking can substantially improve symptoms. These changes often show benefits within weeks.
Medical Devices

CPAP Therapy
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) remains the gold standard treatment. Modern machines are quieter and more comfortable than older models. Various mask styles accommodate different preferences and face shapes.
Oral Appliances
Custom-fitted dental devices can effectively treat mild to moderate sleep apnea. These devices reposition your jaw and tongue to keep airways open during sleep.
Newer Technologies
Auto-adjusting CPAP machines and bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) devices offer more comfortable alternatives for some patients.
Surgical Options
Surgery becomes an option when other treatments fail or aren’t suitable. Procedures range from minimally invasive techniques to more extensive surgeries like uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) or jaw advancement surgery.
Taking Action for Better Sleep Health
Sleep apnea isn’t just about snoring or feeling tired, it’s a serious medical condition that affects your entire body. The warning signs you’ve been ignoring could be your body’s way of asking for help.
Start by honestly evaluating your symptoms. If you recognize multiple warning signs, consider discussing home testing options with your healthcare provider. Many people find that addressing sleep apnea dramatically improves their quality of life, energy levels, and overall health.
Don’t let another night of poor sleep affect your tomorrow. Your body deserves the restorative sleep it needs to function at its best.
FAQs
How accurate are home sleep apnea tests?
Home sleep tests are 80-90% accurate for detecting moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea. They may miss mild cases or central sleep apnea, which is why professional interpretation is important.
Can children have sleep apnea?
Yes, sleep apnea affects children too, often due to enlarged tonsils and adenoids. Symptoms in children may include bedwetting, poor school performance, and behavioral problems.
Will losing weight cure my sleep apnea?
Weight loss can significantly improve or even eliminate sleep apnea symptoms, but it’s not guaranteed. Many factors contribute to sleep apnea, and some people of normal weight also develop the condition.
How long does it take to feel better with treatment?
Many people notice improvements within days to weeks of starting treatment. However, it may take several months to experience the full benefits of consistent therapy.
Is sleep apnea hereditary?
Family history increases your risk, but sleep apnea isn’t directly inherited. Rather, you may inherit physical traits that predispose you to the condition.
Can sleep apnea go away on its own?
Sleep apnea rarely resolves without treatment. In fact, it typically worsens over time without intervention. Early treatment prevents complications and improves long-term outcomes.


